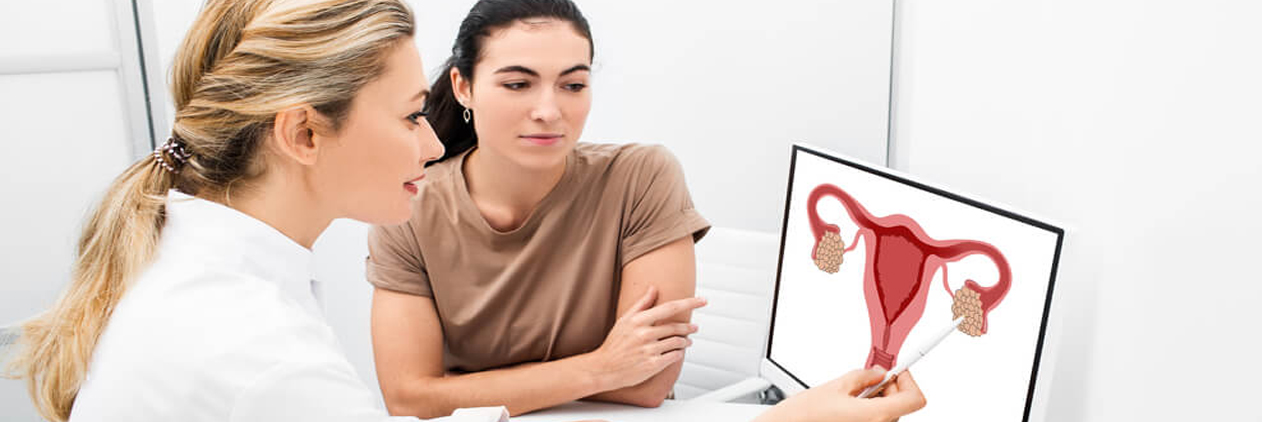
What is female infertility?
Female infertility is the inability of a woman conceive despite frequent and unprotected sexual activity for one year (often one year or more). Getting pregnant or maintaining a pregnancy might be difficult for a woman with this illness
Secondary infertility occurs when a woman had at least one previous pregnancy but is having trouble getting pregnant again. Primary infertility is when a woman has never been able to conceive.
Female infertility can have some different causes, but they include problems with the reproductive system, hormone abnormalities, or other underlying medical diseases.